Thunderbolt 4 is a common interface in Apple computers and some PCs equipped with Intel processors 11th generation and above. Using the same USB-C port as USB 4, Thunderbolt guarantees speeds of up to 40 Gb/s, as well as support for two 4K monitors at 60 Hz, power transfer for battery charging, as well as enough bandwidth to connect to peripherals, external drives, networking, and more via Thunderbolt hubs.
What Thunderbolt is, how it differs from USB 4, and what the overall advantages of the high-speed interface promoted by Intel and Apple over a decade ago are.
What is Thunderbolt?
Thunderbolt is a technology that promotes a high-speed interface on PCs equipped with processors from Intel or Apple. As the result of a partnership between the two manufacturers, the interface emerged as a bet on a new communication platform that offered compatibility with USB but went beyond, ensuring greater performance with much higher bandwidths.
Since the first edition, Thunderbolt was proposed as an interface to meet various use cases: high-resolution video output, high transfer rates to handle large files, and the ability to distribute power to charge devices.

Over successive new generations, Thunderbolt has won praise, but it has never had the same market penetration as more open technologies such as USB. The trend, however, is that the fourth generation of the interface will make this form of connection more popular, given its integration with USB 4.
Similar to USB, newer Thunderbolt standards are perfectly backward compatible.
Differences and similarities with USB 4
Currently, the connector shape of Thunderbolt 4 is the same as that of USB-C, and this naturally opens up room for confusion: USB-C ports can be USB 3, or USB 4, and may not have any compatibility with Thunderbolt technology. Support for Intel’s interface varies from device to device.
Besides the identical connector, there are other similarities: like the high-speed USB 4, the most current Thunderbolt supports the transfer of up to 40 Gb/s (Gigabits per second). We have made the “Hi-Speed USB 4” caveat above because the latest generations of USB come in different specification ranges: there are 20 Gb/s USB 4, for example.
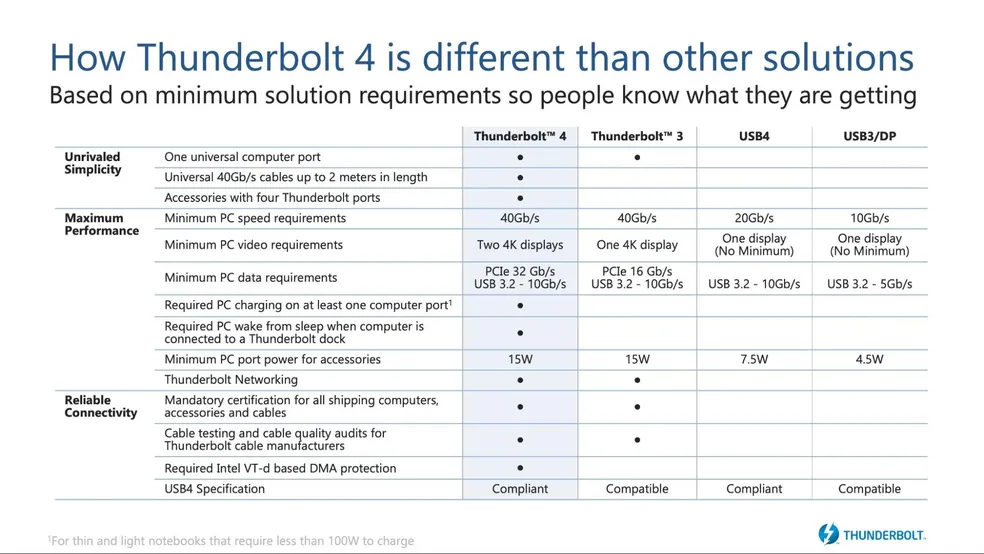
Here is also an interesting comparison: Thunderbolt 4 is unique, while USB 4 is divided into several forms and the consumer doesn’t always take home the best available specification of the interface. This reduces confusion and ensures that all Thunderbolt equipment offers a solid and comparable user experience on different devices.
Both interfaces carry video signals, but Thunderbolt 4 has a clear advantage, capable of controlling two 4K 60 Hz displays – still providing the bandwidth for data exchange. On the flip side, USB 4 is limited to one 4K 60 Hz monitor.
How useful is Thunderbolt 4?
With higher bandwidth and better resourcefulness for carrying image signals, providing the bandwidth for file exchange and power distribution, Thunderbolt 4 has a clear advantage over rival technology in offering hubs that greatly expand a laptop’s functionality.
With a Thunderbolt 4 hub, you sacrifice one port on the laptop but gain multiple video connections, hub-based laptop charging, multiple mainstream USBs, Ethernet connectivity, memory card readers, high-speed external SSDs, and more. USB 4 hubs can have similar functionality, but the limitation of a single monitor, plus lower bandwidth when using video connectivity, end up limiting USB options.
Where to find Thunderbolt ports?
In short, you’ll find Thunderbolt ports on Apple computers and premium notebooks and motherboards with Intel processors: Thunderbolt 4 appears on devices with Core i processors of the 11th generation and later.
In addition to newer Macs and MacBooks, this type of interface appears in notebooks with a more premium profile. In the market, Dell’s Precision and XPS units are examples. The LG Gram, for example, offers Thunderbolt 3.
This post may contain affiliate links, which means that I may receive a commission if you make a purchase using these links. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.

