Ryzen 7 5800H and Intel Core i7 11800H are two high-end processors from AMD and Intel, respectively. Well-known options for gamer notebooks and portable workstations, both CPUs are capable of exceeding 4 GHz of speed and appear in models from Avell, Acer, Dell, and Lenovo. Although they are already being replaced by new generation models from the manufacturers, the processors have a good cost-benefit ratio and are very competitive in performance.
Still, the models end up appearing in laptops with very different price ranges at the moment, especially Intel, which ends up being the cheaper of the two, starting at $395. Thinking about it, Techidence prepared a comparison of the main differences between Ryzen 7 5800H and Intel Core i7 11800H, as well as their technical sheets. Check it out below.
AMD Ryzen 7 5800H vs Intel Core i7 11800H
| Ryzen 7 5800H | Core i7 11800H | |
|---|---|---|
| Launch | January 2021 | May 2021 |
| Price | $395 | |
| Cores/threads | 8/16 | 8/16 |
| Speed | 3.2 to 4.4 GHz | 1.9 to 4.6 GHz |
| overclock | Yes | Yes |
| Memory | Dual-channel DDR4 at 3200MHz | Dual-channel DDR4 at 3200MHz |
| cache | 16 MB in L3 | 24 MB in L3 |
| Video card | Radeon Vega 8 | Intel UHD Graphics |
| TDP | up to 45 W | up to 45 W |
| Socket | soldier on the motherboard | soldier on the motherboard |
Specifications

Core i7 11800H is an 8-core, 16-thread processor, just like Ryzen 7. From a technical standpoint, the two chips differ more in speeds: the AMD goes from 3.2 to 4.4 GHz, while the Core i7 works in ranges of 1.9, 2.3, and 4.6 GHz.
Both CPUs control dual-channel DDR4 memory with speeds up to 3,200 MHz and work with PCIe 4.0 slots, useful in high-performance laptops for connecting to GPUs and SSDs. As for L3 cache memory, there are 24 MB for the i7 and 16 MB for Ryzen.
Another similar feature of the two processors is the presence of an integrated graphics card. The i7 comes with Intel UHD Graphics, while Ryzen comes with Radeon Vega 8. The Radeon is more efficient for heavy graphics applications, but both can control multiple displays and support 4K resolution.
Performance
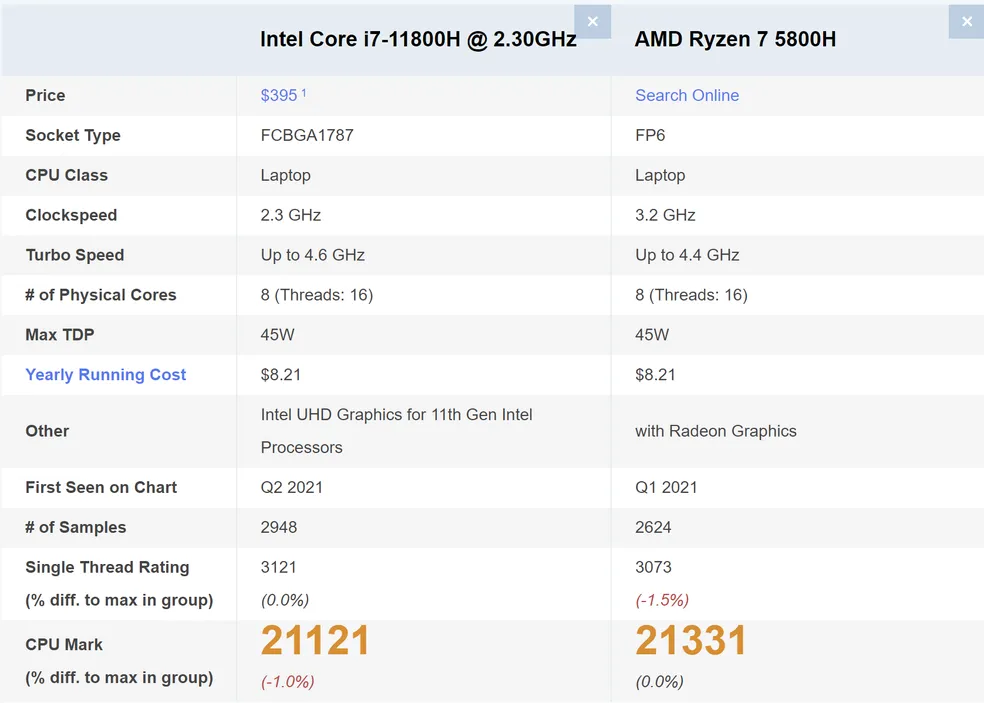
Comparisons between the two processors show that the Intel will be faster if it runs at the maximum supported power. With a TDP of 45 W, the i7 ends up outperforming the Ryzen in the same configuration in applications of many different profiles. AMD, on the other hand, performs better when configured at lower TDPs.
In CPU Benchmark, the consolidated scores of the two chips are 21,331 points for AMD and 21,121 for Intel’s unit – a difference of just 1%. This pattern is repeated in comparison to running games. Jarod’s Tech channel ran tests with several games and recorded averages of 117 FPS with the Intel running Fortnite at 1440p and on “high,” while the AMD hit 113 FPS in the same scenario.
In Cyberpunk 2077, with Ray Tracing mode in ultra and Full HD, the averages registered a technical tie: the Core went to 58.23 against 58.24 of the Ryzen 7.
Consumption

As they are laptop processors, the two units have a similar profile when it comes to power. Both have a maximum TDP of 45 W, plus smaller ranges of 25 and 35 W, which can be configured by manufacturers. Those who opt for a more aggressive design, unable to handle much heat, can mount the processor in a lower power band, which reduces heat but also cuts CPU performance.
Since the numbers are similar, what will determine the real consumption of each processor in each notebook are design issues defined by each brand in the market.
Pricing and Competitors
Between the two products, the Core i7 appears in cheaper laptops: the most affordable model equipped with the processor is Acer’s Nitro 5. The Ryzen appears in the Lenovo Legion Slim, Lenovo’s gamer model with more sophisticated hardware.
Processor options for these two models exist in the form of new generations of Intel or AMD – and even previous generations, for those who give up technology in performance in favor of better prices.
This post may contain affiliate links, which means that I may receive a commission if you make a purchase using these links. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.

