GPU and APU are processing units that perform dedicated video enhancement functions on computers and laptops. Video cards, as GPUs are known, are responsible for processing the machine’s graphics information and setting the level of performance in games and tasks such as video editing or animation. APUs, on the other hand, is an invention by AMD to combine GPU and CPU in a single device, and are a cost-effective alternative for those who want to build a powerful machine but don’t have that much money to spend.
Choosing between the two, however, depends on the user’s personal needs. While GPUs tend to be more robust and are present in a large number of options on the market, AMD APUs may be suitable for functions that require intermediate performance. We have separated the main differences to help you choose.
Before continuing, for a better understanding of the subject, it is necessary to elucidate what a CPU is for. The “Central Processing Unit” is the key unit of a computer. Because it has several cores, it works like a brain, being responsible for basic commands, such as the very act of loading the operating system, opening the internet browser, or any program. This implies that all functions performed by the RAM go through the CPU, without exception.
What is the GPU used for?

The “Graphics Processing Unit”, or video card, remains dedicated to video activities, processing the computer’s 2D and 3D graphics information. Generally, this is one of the main components for those who want a gaming computer. This is because games require a high visual capacity, and the faster the video card processes the information, the more frames are obtained every second.
By acting in parallel to the CPU, video processors prevent the machine from overloading, since they use their power budget, cooling, and RAM, resulting in higher device speed and less stress for the user.
In more detail, when a computer has a CPU and a GPU working together, the former can concentrate on the general management of the machine, handling many different sectors, like in a company. Meanwhile, the GPU takes care of its sector and can use all its engine power to improve the performance of games and heavier programs like video and image editors.
What is the APU used for?
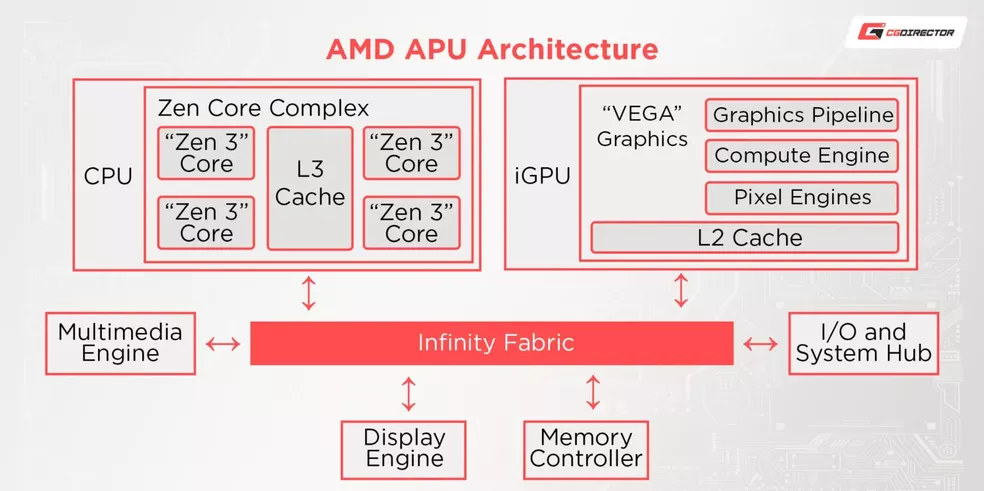
The “Advanced Processing Unit”, on the other hand, is a class of AMD chips that seeks to replace the conventional CPU and GPU. The idea is that the two parts are inserted into a single component to take up less space and reduce the cost of the product. This technology works by combined processing of the two parts, with faster and greater data exchange in an integrated fashion.
Although the performance of the APU may seem better since it is designed to speed up processing, it can leave a lot to be desired when high performance for heavy gaming or programs is expected. However, if the purpose is an economical computer that can run light games and simple image and video editing tasks, it can still be a good option.
Another advantage of APUs is lower power consumption compared to a simple CPU + GPU combination. This is because there are fewer transistors to power and no extra fans or fancy LEDs. In the case of notebooks, they can also offer longer battery life.
APUs can use a considerable amount of system memory for graphics processing, around 2 to 4 GB of memory. Thus, it is recommended that the computer has at least 16 GB of RAM installed in a dual-channel configuration to ensure stable performance.
GPU or APU: Which one to invest in?

If the computer is to use not-so-heavy programs, computers and laptops with APU may be the best option. If the intention is still to play, but the budget is also low, there are some options to build a gaming PC with AMD that promises good value for money. A positive point is that the APUs are GPU compatible, which can be an attractive tactic for beginning gamers, since in the future it may be necessary to install a dedicated card.
Although some AMD chips are advancing technologically, APUs will not replace the resourcefulness of two conventional high-performance parts. GPUs are designed to perform a high volume of repetitive calculations. To make this happen, they have billions of transistors that process information at once. There is no strict limit to the space available on a GPU, unlike APUs where the number of transistors is significantly smaller.
In addition, dedicated graphics cards also have better cooling and memory, known as VRAM (Video Random Access Memory). This memory is a special type that can be accessed directly on the graphics cards and guarantees data transfer at higher speeds.
This post may contain affiliate links, which means that I may receive a commission if you make a purchase using these links. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.

