RTX 3050 is Nvidia’s new entry-level dedicated card for mid-range laptops, taking over from the RTX 3060. The two versions are similar in technology, with support for real-time hardware Ray Tracing and upscaling via DLSS 2.0. In raw performance, the advantage goes to the RTX 3060, capable of running recent Full HD games with high graphics quality and FPS rates above 60. Below, see the datasheet of both cards, differences, and laptop models where you can find them.
Nvidia GeForce RTX 3050 vs GeForce RTX 3060
| Specifications | GeForce RTX 3050 | GeForce RTX 3060 |
|---|---|---|
| Launch | May 2021 | February 2021 |
| Cores | 2,048 CUDA | 3,840 CUDA |
| Speed | 1,057 to 1,740 MHz | 1,283 to 1,703 MHz |
| RAM | 4 GB GDDR6 | 6 GB GDDR6 |
| Memory speed | 14 Gb/s | 14 Gb/s |
| Memory interface | 128 bits | 192 bits |
| Bandwidth | 192 GB/s | 336 GB/s |
| TGP | from 35 to 80 Watts | from 65 to 115 Watts |
Specifications
Both cards belong to the same Nvidia generation and this means that they share the same Ampere architecture. The differences are in the processing power of both, with the RTX 3060 offering more cores and thus higher performance.

The more powerful card has a total of 3,840 graphics processing CUDA cores, which are the units responsible for the raw graphics processing of the card. The RTX 3050, on the other hand, has a smaller GPU, equipped with a total of 2,048 cores.
The speed range also differs for both, considering here the faster versions of the cards. The RTX 3060 operates between 1,283 and 1,703 MHz, while the RTX 3050 goes from 1,057 to 1,740 MHz. The difference may seem small, but this is where the RTX 3060’s higher number of cores translates into higher performance: 3,840 cores at 1,703 MHz will be faster than 2,048 at 1,740 MHz.
In addition to CUDA, the two processors offer some specialized components: the RTX 3060 comes with 30 RT cores, responsible for Ray Tracing acceleration, as well as 120 Tensor cores, used for AI processing, in particular for DLSS 2.0. The RTX 3050 comes with 16 RT and 64 Tensor units.
With regards to RAM, the advantage once again lies with the RTX 3060: the card will have access to 6 GB of dedicated GDDR6, connected to the graphics processor via a 192-bit interface, resulting in a rate of information exchange between GPU and memory in the region of 336 GB/s. The RTX 3050 comes with less VRAM – 4 GB – and offers lower bandwidth of 192 GB/s via 128-bit.
Performance
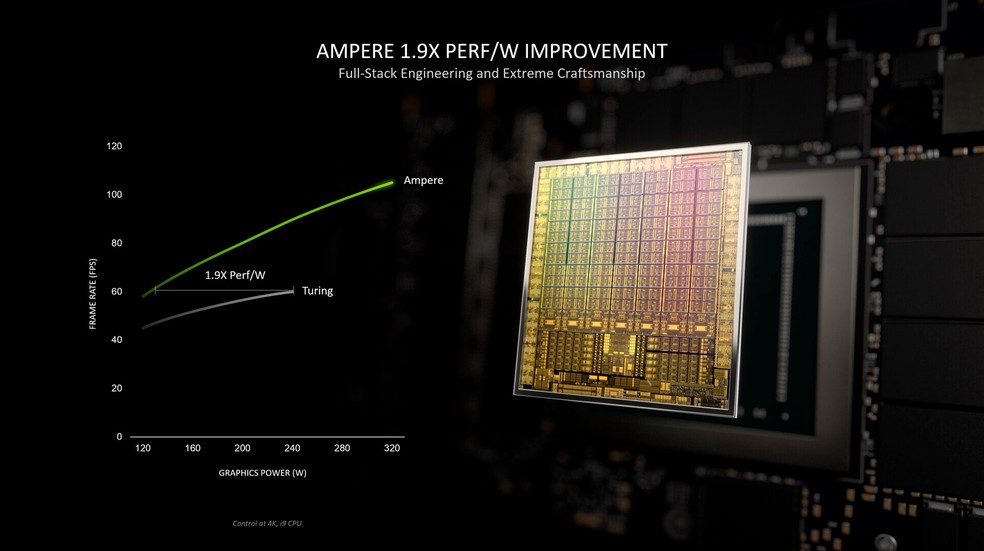
Before discussing performance data for the two cards, it is important to keep in mind the variations of the RTX 3050 – as well as the RTX 3060 – on the market. Nvidia offers these cards in various power and consumption ranges, which means that manufacturer A may use an RTX 3050 in its most powerful version to the point where it rivals manufacturer B’s laptop equipped with a more affordable RTX 3060.
Another caveat is that the RTX 3050 was recently announced, meaning that data on its performance and actual comparisons are still lacking. Estimates from NotebookCheck, however, indicate that the RTX 3050 should guarantee graphics performance that would be between the older GTX 1650 Ti and GTX 1660 Ti.
The RTX 3060, on the other hand, is older in its mobile version and tests suggest that it achieves comparable performance to the RTX 2070 Super. Tests from sites like NotebookCheck and TechSpot have measured numbers such as an average of 48.7 fps in Hitman 3 in 4K, 74.2 fps in Dirt 5 running in Full HD, and overall averages that show the RTX 3060 up to 72% faster than the RTX 2060 for laptops. It is important to remember that these values are directly sensitive to the version of the card chosen by the laptop manufacturer: lower power versions will have lower performance.
Features
Both RTX is part of the Ampère architecture and brings with them some features unique to this generation of Nvidia. For example, there is support for Ray Tracing with second-generation technology, something that will allow access to more realistic lighting effects and simulation of light, shadows, and reflections in games.

Another common virtue of the two cards is the support for DLSS 2.0. This technology uses artificial intelligence to transform the image generated by a game in low resolution – such as Full HD – to a superior result on the screen, all without loss of quality or performance.
Consumption
The discussion about the power consumption of Nvidia Ampere in laptops is not simple: there are 28 different versions of the Ampere cards, considering only RTX 3080, RTX 3070, and RTX 3060 in laptops. In specifications – processor and RAM – they are all the same, what changes is the amount of power each one consumes.

In the case of the RTX 3050, there are seven versions: 35, 40, 45, 50, 60, 70, and 80 Watts. Naturally, the 80-Watt option will be faster than the others, but it will heat up considerably more and use much more battery power. The RTX 3060 has similar targeting, but in a higher consumption range, ranging from 60 to 115 Watts.
Nvidia has required laptop manufacturers to be transparent about exactly which card is being used. The recommendation is to look for data that can be categorized as TGP (which is an Nvidia metric to indicate the maximum power required by the GPU to function) or TDP.
Also, it is important to keep in mind that versions with lower values will have lower performance – although they may save battery power and produce less heat.
Cost-benefit
RTX 3050 and RTX 3060 are cards that are close in specifications, but very different in terms of audience and performance potential. The RTX 3050, especially in the cheaper versions, should be bet by manufacturers in more expensive notebooks – something like Lenovo ThinkPad and Dell XPS 15 – but without gamer appeal, while the RTX 3060 appears more often in intermediate gamer notebooks.

Faster versions of RTX 3050, with higher TGP, should appear in entry-level gamer notebooks, a common profile in the market in series such as Acer’s Nitro 5, Dells G3 and G5, or Samsung’s Odyssey.
In any case, apart from the discussions related to the confusion of different versions with the same name and specifications, both RTX 3050 and RTX 3060 can be good bets for those who need a laptop with good graphics performance: the offer of features such as Ray Tracing and DLSS 2.0 make them more complete proposals than the GeForce GTX 1650 and GTX 1660.
This post may contain affiliate links, which means that I may receive a commission if you make a purchase using these links. As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.

